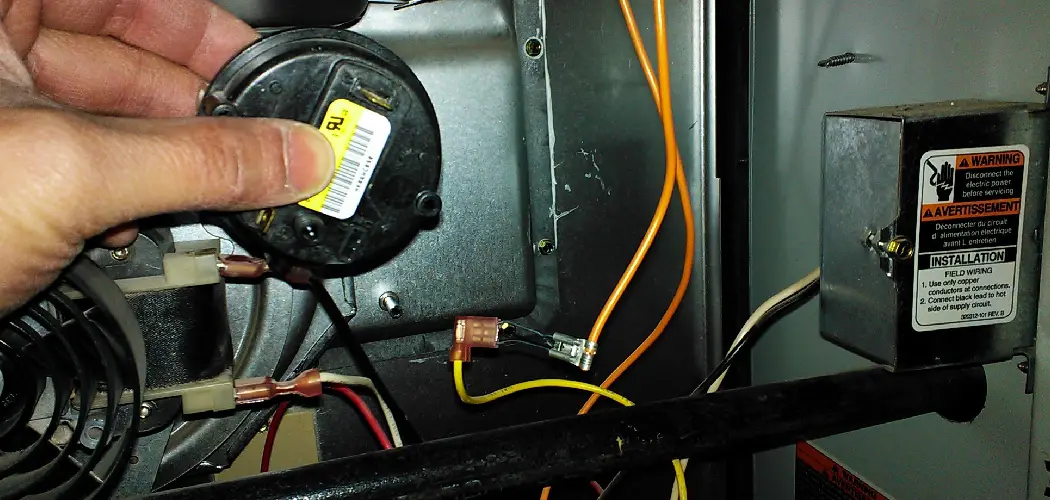
The pressure switch plays a pivotal role in maintaining your furnace’s safe and efficient operation. Acting as a critical safety device, it monitors the airflow or pressure within the furnace’s venting system, ensuring that combustion gases are properly expelled outside.
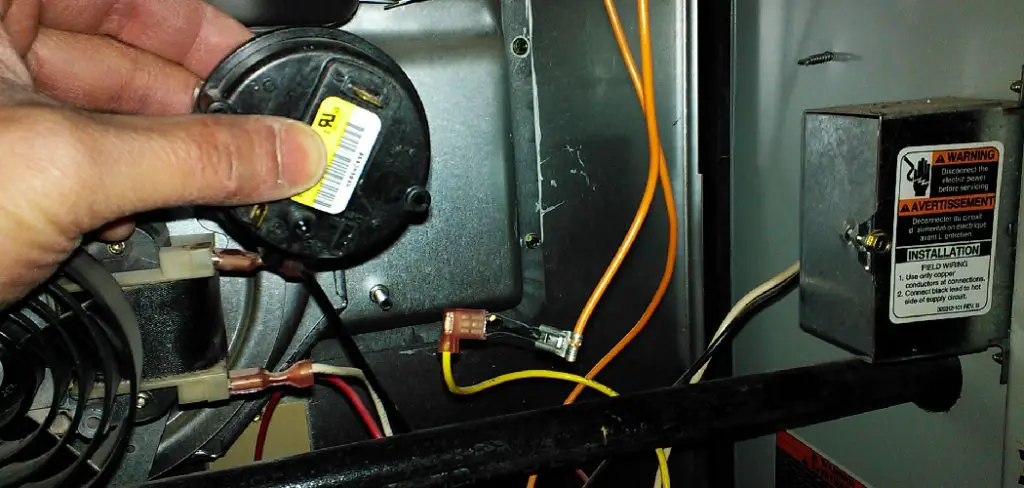

A malfunctioning pressure switch can lead to a range of furnace problems, including failure to ignite or shut down mid-cycle. It can pose significant safety hazards, such as the risk of carbon monoxide buildup within the home, and may cause extensive system damage over time. Understanding how to test a furnace pressure switch is essential for homeowners looking to maintain their furnace’s performance and ensure the safety of their home environment.
The Function of the Pressure Switch
The pressure switch is a crucial component in operating a typical gas furnace. Its primary function begins when the burner ignition process initiates. This action triggers the draft inducer fan to start, which, in turn, creates a negative pressure within the venting system.
The pressure switch is designed to sense this drop in pressure and, upon detecting it, sends a signal to the furnace’s control board. This signal is vital because it informs the control board that the venting system is clear, allowing it to safely allow gas flow to the burners for combustion.
Once the combustion process stabilizes the pressure in the system, the furnace continues its operation cycle, ensuring efficient and safe heating of the home. This orchestrated sequence highlights the integral role of the pressure switch in maintaining the furnace’s safety and functionality.
Types of Furnace Pressure Switches
There are primarily two main types of pressure switches used in furnace systems. The first type is the Single Pole, Single Throw (SPST) switch. These switches operate on a simple mechanism, opening or closing the circuit based on the pressure sensed in the system. They are straightforward in their function, either allowing or stopping the operation based on the safety conditions they monitor.
The second type is the Differential Pressure Switch. Unlike the SPST switches, differential pressure switches monitor the pressure difference between two points within the system.
This allows for a more nuanced control and monitoring of the furnace’s operation, ensuring that the system maintains optimal performance and safety by reacting to even slight changes in pressure. These two types of switches are foundational to the diverse operational contexts of modern furnaces, tailoring their functions to specific system requirements.
Signs of a Faulty Pressure Switch
When it comes to furnace performance issues, several signs could indicate a problem with the pressure switch. Homeowners might notice that the furnace fails to ignite or shuts down unexpectedly during operation. This can often happen if the pressure switch is not correctly sensing the pressure changes in the furnace’s venting system, preventing the furnace from continuing its cycle.
Additionally, if the burner continues to operate even after the thermostat has indicated the heating cycle is complete, it might suggest a malfunction within the pressure switch mechanism. More worrying signs include sooting around the furnace or the presence of carbon monoxide, which are significant safety hazards requiring immediate consultation with a professional.
Furthermore, modern furnaces often have control panels that display various error codes when issues arise. Consulting the furnace manual for specific meanings of these codes can help identify if the problem relates to the pressure switch or another component.
Importance of Identifying the Issue
A faulty pressure switch is only one potential cause of furnace operation issues. However, it’s a critical component affecting the safety and efficiency of your heating system. Before jumping to conclusions, it’s essential to rule out other possible problems. These may include a clogged flue that impedes proper venting or a dirty filter restricting airflow.
Identifying the specific issue is crucial, as it ensures that any maintenance or repairs are accurately targeted, avoiding unnecessary work and costs. Correctly diagnosing the problem is the first step toward a safe and efficient heating system.
Safety Precautions Before Testing
Adhering to stringent safety measures is critical to avoid accidents and injuries when testing or troubleshooting your furnace’s pressure switch. One of the most fundamental steps is ensuring that the furnace system is completely powered down before beginning any form of inspection.
This involves initially turning off the furnace at the thermostat and then switching off the power supply directly from the circuit breaker or fuse box. This two-step shutdown process guarantees that the furnace does not accidentally activate while servicing, preventing potential electrical shocks or equipment damage.
Another pivotal safety aspect is conducting testing or repairs in a well-ventilated area. Furnaces, especially gas-powered ones, can emit dangerous fumes such as carbon monoxide, which can be harmful if inhaled in confined spaces. Ensuring that the area around the furnace is well-ventilated mitigates the risk of gas fume accumulation, safeguarding your health during the process.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) cannot be overlooked when dealing with furnace maintenance. The use of gloves and safety glasses is highly recommended to protect against unforeseen hazards, such as sharp edges within the furnace’s interior and any particulate matter that could be dislodged during the inspection process. These items provide a necessary barrier against physical harm, ensuring that safety is maintained throughout the testing procedure.
Lastly, if the inspection or troubleshooting process requires direct interaction with the furnace’s internal components, shutting off the gas supply valve might be necessary. This step is crucial to avoid gas leaks or exposure while working on the system. If there is any uncertainty about properly shutting off the gas supply or the situation seems risky, it is imperative to consult a professional. A qualified technician can provide guidance or take over the task to ensure it’s done safely and correctly.
Overall, adhering to these safety precautions lays a strong foundation for a safe and effective troubleshooting process. Remember, the goal is to identify and remedy issues with your furnace’s pressure switch and ensure that the procedure is carried out without endangering yourself or others. If at any point the task seems beyond your comfort level or expertise, do not hesitate to seek professional assistance.
Tools and Resources Needed for Testing
When venturing into the territory of testing or troubleshooting your furnace’s pressure switch, equipping yourself with the right tools and resources is essential for an accurate and safe process. Some of the indispensable tools you will need include:

- Multimeter: A key tool in your arsenal, the multimeter, is indispensable for diagnosing electrical issues within your furnace system. This versatile instrument measures various electrical properties such as voltage, current, and resistance. Specifically, for pressure switch testing, its ability to check for electrical continuity—whether an electrical path is complete or not—is crucial. It can also help verify that the pressure switch is receiving the correct voltage, ensuring the operational integrity of the switch.
- Manometer (Optional): While not required for all testing procedures, a manometer can be invaluable when measuring the pressure difference that the switch is supposed to detect. This can help confirm whether the pressure switch is accurately sensing changes in the system, especially in complex scenarios.
- Flashlight: Given the often dimly lit spaces where furnaces reside, a flashlight is essential for visibility and accurately locating and assessing the pressure switch and surrounding components.
Beyond these tools, a deep understanding of your specific furnace model is imperative. Consulting your furnace manual should be your initial step. This resource often contains details specific to the model you own, including schematics, specifications for electrical supply, and troubleshooting tips tailored to your system. If the manual is unavailable, the manufacturer’s website frequently offers digital copies or additional troubleshooting advice.
For those with more technical expertise or facing more complicated issues, obtaining a service manual for your specific furnace model might be beneficial. This manual provides more in-depth information, including detailed diagrams, service codes, and advanced troubleshooting steps. These manuals can sometimes be acquired directly from the manufacturer or found online through forums or specialized websites.

Armed with the right tools and informed by the proper resources, you’re now better positioned to safely and effectively test and troubleshoot your furnace’s pressure switch. However, remember that working with electrical components and gas appliances presents inherent risks.
If the testing process feels overwhelming or dangerous at any point, consulting with a professional technician is highly advised. Their expertise can ensure that the job is done safely and correctly, helping to restore your furnace to optimal operation without compromising safety.
Visually Inspecting the Pressure Switch
Before proceeding with electrical testing, conducting a thorough visual inspection of the pressure switch is critical to identify any visible signs of damage or wear. This initial step is crucial because physical damage to the switch can be an indicator of underlying issues that might affect the functionality of your furnace system.
Begin by examining the pressure switch for any obvious cracks or signs of burning, which could signal previous electrical overloads or failures. Additionally, look for any signs of corrosion on the switch body or its connections, as this can interfere with the switch’s ability to operate correctly.

Loose connections, both on the switch body and the hoses attached to it, should also be scrutinized. These could compromise the switch’s ability to detect pressure changes accurately, leading to operational issues with your furnace.
If any damage is visible, replacing the pressure switch immediately is advisable. Continuing to use a damaged switch not only risks the efficiency and reliability of your furnace but can also pose significant safety hazards.
Consulting with a professional is recommended for any doubts or if the inspection reveals complex issues. A qualified technician can provide further troubleshooting, ensuring that any replacement or repairs are performed safely and accurately, thereby restoring the proper function of your furnace system without compromising safety.
How to Test a Furnace Pressure Switch: Testing the Pressure Switch (Electrical Methods)
A. Using a Multimeter
1. Continuity Test
To perform a continuity test using a multimeter, the first step is to ensure the device is set to the continuity setting, typically represented by a horseshoe or similar symbol. Before proceeding, as a precautionary measure, it is crucial to turn off the power to the furnace again, even if it has been turned off previously. Carefully disconnect the wires from the terminals of the pressure switch, consulting the furnace’s manual to correctly identify these connections.
Once the wires are disconnected, take the multimeter probes and touch one to each terminal on the pressure switch. Observing the meter reading is key; a continuous beep or sound from the multimeter indicates a closed circuit, meaning the switch is currently activated.
Conversely, the absence of sound signifies an open circuit, indicating the switch is not activated. This simple test is essential for assessing whether the pressure switch is functioning as intended by confirming its ability to open and close under appropriate conditions.
2. Optional: Resistance Test
Some pressure switches may require a resistance test for a more detailed analysis, especially if the manufacturer provides specific specifications. To conduct this test, set the multimeter to the ohms setting, represented by the omega symbol.
Following the same initial steps as in the continuity test, ensure the power is off, and the wires are disconnected from the switch terminals. Place one multimeter probe on each terminal and read the measurement. The results of this test are determined by comparing the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications, which can typically be found in the furnace manual or through online resources.
A measurement within the specified range indicates a functional switch, whereas a reading that falls outside this range or shows zero suggests a malfunctioning component. This resistance test adds a layer of specificity to the diagnostics by quantifying the switch’s electrical resistance, which is crucial for precisely verifying its operational integrity.
B. Limitations of Electrical Testing
While conducting electrical tests on the pressure switch using a multimeter can yield valuable insights into the switch’s functionality, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations of these methods. The electrical tests primarily assess the switch’s ability to conduct electricity, but they might not capture internal issues affecting its ability to sense and respond to pressure accurately.
For instance, the switch could exhibit correct electrical behavior but still fail to actuate due to mechanical problems or incorrect pressure sensing. Therefore, these electrical tests, though crucial, are just one component of a comprehensive troubleshooting approach. Further inspection and possibly professional consultation may be necessary to thoroughly evaluate the switch’s performance and the overall health of the furnace system.
How to Test a Furnace Pressure Switch (Optional: Manometer Method)
Manometers, essentially pressure gauges, are sophisticated tools employed to precisely measure pressure differences, often in various gases or liquids. This intricate instrument compares the pressure of the gas within the furnace against a known reference pressure, thereby accurately determining the existing pressure level. Testing a furnace’s pressure switch requires not only the device itself but also a profound understanding of its function and the system used to diagnose it.
It is imperative for homeowners, particularly those lacking a technical background, to first consult their furnace’s manual or engage the assistance of a qualified professional before attempting to use a manometer.
Several furnace models outline specific instructions on how to correctly attach a manometer to certain ports on the venting system, a step that varies significantly across different models and manufacturers. This careful preparation ensures the accurate capture of pressure readings correlated directly with the operation of the furnace.
Once correctly installed, the manometer will display the pressure readings during the furnace’s operation, which should then be meticulously compared against the specifications detailed within the furnace’s manual. An alignment of these readings with the manual’s specifications typically signals a functional pressure switch, ensuring the furnace’s efficient and safe operation.

On the contrary, significant deviations from these prescribed values could hint at potential issues, either with the pressure switch itself or possibly with the venting system at large. Such discrepancies, especially those not resolved through basic troubleshooting steps, necessitate further evaluation by a heating system professional.
It’s crucial to underscore the importance of safety and precision when using a manometer. This method, reserved for advanced users or qualified professionals, offers a detailed insight into the furnace’s operational pressures, providing a comprehensive analysis beyond what can be gleaned from electrical testing alone.
However, due to the potential complexities and risks, seeking professional help is recommended for those unfamiliar with these procedures to ensure their heating system’s continued safe and effective usage.
Interpreting Test Results and Next Steps
The tests outlined above, including the continuity, resistance, and manometer methods, are designed to give homeowners a clearer picture of their furnace’s pressure switch condition. Understanding the results is crucial for deciding on the next steps. Typically, if the continuity test indicates a closed circuit (with the multimeter beeping), the switch is functioning correctly at that moment.
However, a lack of sound signifies an open circuit, suggesting the switch may not work as intended. Similarly, resistance measurements that fall within the manufacturer’s specified range point towards a functional switch, while readings outside this range suggest a malfunction.
However, it’s important to remember that a faulty pressure switch is only one possible culprit in a malfunctioning furnace system. Other issues, such as a clogged flue, dirty filters, or problems within the venting system, can also trigger similar symptoms. Therefore, pinpointing the exact cause can be complex, requiring a more detailed evaluation than these initial tests provide.
If the tests indicate a potential problem with the pressure switch, or if you, as the homeowner, feel unsure about diagnosing and addressing furnace issues, it’s strongly recommended to consult a qualified HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) professional. An expert can offer a more in-depth analysis, considering the pressure switch in the context of the entire heating system, and identify any additional underlying problems.
Potential repair options might include replacing the pressure switch itself if it’s conclusively diagnosed as faulty. However, if the issue lies within the furnace system’s venting or airflow, troubleshooting could range from cleaning the flue and filters to adjusting or repairing the venting system. Each of these solutions requires a specific set of skills and tools, underscoring the importance of professional assistance.
In summary, while a homeowner can perform initial diagnostics to identify issues with the furnace’s pressure switch, interpreting the results and undertaking repairs often necessitate a more experienced hand.
Whether the tests point directly to a faulty pressure switch or hint at broader system issues, enlisting the aid of an HVAC professional ensures a safe, correct, and efficient resolution. This approach not only addresses the immediate problem but also aids in maintaining the longevity and performance of your heating system.
Safety Reminders and Conclusion
While exploring how to test a furnace pressure switch, it is crucial to prioritize safety above all. Diagnosing or repairing your furnace can be dangerous without proper knowledge and precautions.
Always ensure the furnace power and gas supply are turned off before starting any tests or repairs to avoid accidents. The complexity of these systems means that what starts as a simple procedure can quickly escalate without the correct safety measures in place.
This guide underscores the importance of a properly functioning pressure switch for your furnace’s safe and efficient operation. A malfunctioning switch can compromise the system, leading to potential safety hazards and decreased performance.
Therefore, even if you feel comfortable conducting preliminary tests, consulting with a qualified HVAC professional for detailed diagnostics and repairs or if any part of the process is unclear is always the best course of action.
In conclusion, maintaining the health of your furnace is not just about fixing immediate issues but also about preventing future problems. Regularly scheduled maintenance by a qualified technician is essential in ensuring your heating system’s longevity, safety, and efficiency. By taking these proactive measures, you ensure a warm, comfortable home and peace of mind knowing your system operates safely.

