A pipe clamp is a versatile fastening device that securely holds pipes in place. It is an essential tool across various fields, including plumbing, woodworking, metalworking, and industrial applications. Pipe clamps are designed to provide support, stability, and alignment for pipes, ensuring the safety and efficiency of projects.
Understanding how to connect a pipe clamp properly is crucial for achieving a secure and reliable fit. The connection process involves selecting the correct type of clamp for the pipe, positioning it accurately, fastening it firmly, and testing the stability of the connection.
Each step ensures the pipe is held securely without compromising its integrity or function. Whether you are installing plumbing systems, building a woodworking project, or assembling industrial equipment, knowing how to connect a pipe clamp is a fundamental skill for successful outcomes.

Types of Pipe Clamps and Their Applications
Standard Pipe Clamps
Standard pipe clamps are widely used for securing plumbing and HVAC pipes in residential and commercial settings. These clamps provide a reliable grip to keep pipes in place, ensuring efficient water flow and preventing unnecessary movement. Their straightforward design makes them an essential component for maintaining organized and stable plumbing systems.
Adjustable Pipe Clamps
Adjustable pipe clamps are commonly used in woodworking and similar projects requiring flexibility. These clamps are ideal for holding materials together, such as wooden boards, during gluing or assembly. Their adjustable feature allows users to accommodate varying sizes of materials, making them a versatile tool in workshops or construction environments.
Cushioned Pipe Clamps
Cushioned pipe clamps feature a padded lining that helps reduce vibrations, noise, and wear caused by mechanical movements. They are commonly used in mechanical and industrial systems where pipes or tubing transport fluids or gases under pressure. The cushioning protects the pipes and enhances the overall system’s efficiency by minimizing disruptions.
Heavy-Duty and Rigid Pipe Clamps
Heavy-duty and rigid pipe clamps are specifically designed for industrial, structural, and construction applications. These clamps provide superior stability and support for large-diameter pipes or heavy pipes carrying significant loads. Their robust construction ensures durability and safety, even in demanding environments.
Tools and Materials Needed
Essential Tools
To effectively work with pipe clamps, having the right tools is crucial. A wrench, screwdriver, tape measure, and drill (if mounting) are the primary tools you’ll need for installation and adjustments. These tools ensure precise measurements and secure fastening of the clamps to the intended surface or structure.

Required Materials
When installing or using pipe clamps, the necessary materials include the pipe clamp itself, screws or bolts for fastening, and rubber padding if additional cushioning or noise reduction is required. The rubber padding can prevent wear on both the pipe and the clamp, especially in systems subject to vibrations or movement.
Choosing the Right Clamp Size
Selecting the correct pipe clamp size is essential for ensuring a secure fit and preventing any movement or instability. Measure the pipe’s diameter accurately with a tape measure and match it to the designated clamp size specifications. Using an appropriately sized clamp minimizes the risk of damage and supports the system’s structural integrity. This careful selection process results in a more stable and efficient installation.
Positioning the Pipe and Clamp
Measuring and Marking the Clamp Placement
Proper placement of the clamps begins with accurate measuring and marking along the mounting surface. For single clamps, identify where the pipe will be positioned and measure the distance to ensure alignment with existing structures.
When installing multiple clamps, it is crucial to maintain even spacing between them to distribute weight evenly and avoid unnecessary stress on the pipe or the surface. A pencil or marking tool can be used to indicate the positions, providing a clear guide during installation.
Ensuring Even Spacing for Multiple Clamps
When working with longer pipes or systems requiring several clamps, calculate the required spacing based on the pipe’s weight, length, and the system’s overall design. Uneven spacing can create weak points, leading to potential sagging or instability.
As a rule, clamps should generally be placed at intervals that do not exceed six to ten feet for straight piping, with adjustments made for heavier or more flexible materials. Consistent spacing enhances both functionality and aesthetics, ensuring a neat and professional installation.
Aligning the Pipe Properly
To avoid unnecessary stress points and ensure system longevity, keeping the pipe level parallel to the mounting surface is essential. Use tools like a spirit level to verify that the pipe is straight, making adjustments as needed before fastening the clamps.
Misaligned pipes can lead to uneven pressure distribution, increased wear, and potential failure of the system. By taking the time to align the pipe properly, you safeguard both its integrity and performance over time.

Using a Support Bracket for Heavy Pipes
For heavier piping systems or extended pipe lengths, support brackets should be used in addition to clamps to prevent sagging and ensure stability. Support brackets are particularly important in systems where the pipe carries significant weight, such as drainage or industrial setups.
These brackets provide additional strength to the system, reducing stress on individual clamps and maintaining the proper orientation of the pipe. Integrating support brackets creates a more secure and durable installation capable of withstanding long-term use and environmental factors.
Securing the Pipe Clamp
Fastening with Screws or Bolts
Properly fastening the pipe clamp is critical to ensuring the stability and functionality of the system. Begin by selecting appropriate anchors based on the surface where the clamp will be mounted. For walls, toggle bolts or wall anchors are suitable for hollow surfaces, while masonry anchors may be needed for concrete or brick.
For ceiling or floor installations, heavy-duty expansion bolts or lag screws might be necessary, particularly for heavier pipes. Position the clamp against the surface and mark the holes for mounting. Drill pilot holes as needed, then securely fasten the clamp using screws or bolts, ensuring a snug fit. Double-check that the anchor type is rated to handle the weight and stress of your pipe system over time.
Tightening the Clamp Evenly
When tightening the clamp around the pipe, applying even pressure is essential to prevent twisting or misalignment. Most clamps include a screw or bolt mechanism that draws the two halves of the clamp together. Begin by tightening the screw or bolt until the pipe is secured in place but still movable. Gradually tighten both sides of the clamp alternately, checking the alignment of the pipe as you go.
This method ensures that the pressure is distributed evenly along the pipe, reducing the risk of damage and ensuring a firm grip. Avoid rushing this step, as uneven clamping could compromise the stability of your installation.
Preventing Over-Tightening
Over-tightening the clamp can lead to unintended consequences, such as deforming the pipe material or creating unnecessary stress points. Particularly for pipes made from softer materials like plastic or PVC, excessive force may cause cracks or other structural weaknesses.
Tighten the clamp only until it secures the pipe firmly without restricting its natural movement or flexibility. Using a torque wrench can help maintain consistent pressure and avoid over-tightening.
Checking for Movement and Adjustments
Once the clamp is secured, test the installation by gently applying moderate pressure to the pipe. This step will confirm that it’s held securely and does not shift out of alignment when subjected to typical forces. If movement is detected, reassess the alignment of the pipe and re-tighten the clamp as needed.
Ensure there’s still a small allowance for thermal expansion or contraction in systems exposed to temperature fluctuations. Properly checking for adjustments ensures a secure installation while preserving the functionality and longevity of your piping system.

Testing the Connection and Making Adjustments
Inspecting for Stability
After securing the pipe clamp and ensuring proper alignment, it’s time to test the connection for stability. Begin by visually inspecting the area for any loose fittings or misalignments that might compromise the system’s integrity. Carefully check that the pipe remains steady and that all components are properly seated.
Making Adjustments if Necessary
If you notice any issues, such as slight shifts or uneven positioning, it may be necessary to make adjustments. Loosen the clamp slightly to reposition the pipe, ensuring that it remains properly aligned.
Once the corrections are made, re-tighten the clamp, taking care not to overtighten. Double-check that the pipe has adequate support without being overly restricted, allowing for operational flex and thermal expansion if applicable. This final step ensures a secure, reliable connection that minimizes future maintenance needs.
Common Mistakes to Avoid on How to Connect a Pipe Clamp
Using the Wrong Clamp Size
Choosing an incorrect clamp size is a common error that can jeopardize the connection’s stability. A too loose clamp will fail to secure the pipe effectively, leading to movement and potential leaks. On the other hand, an overly tight clamp may cause unnecessary stress on the pipe and adjoining components, compromising the system’s durability.
Over-Tightening the Clamp
While ensuring a firm connection is crucial, over-tightening the clamp can result in significant damage. Excessive force may deform the pipe, leading to cracks or weakened integrity over time. Always exercise caution and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to avoid unnecessary breakage or stress on the material.
Ignoring Proper Pipe Support
For heavier pipes, a single clamp may not offer sufficient support. Without additional clamps or reinforcement, the weight of the pipe can lead to sagging or strain on nearby connections. Ensure proper distribution of support to maintain both alignment and functionality.
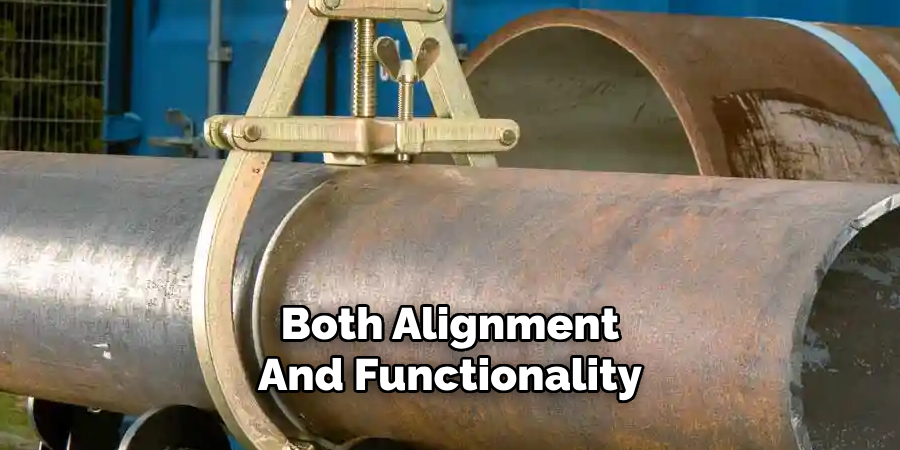
Conclusion
Understanding how to connect a pipe clamp correctly is essential for maintaining a secure and reliable system. By carefully selecting the appropriate clamp size, positioning it accurately, and securing it with the right amount of force, you can prevent common issues such as leaks, sagging, and material damage.
Regularly testing the connection ensures long-term stability and functionality. To achieve the best results, always opt for high-quality clamps and adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Following these key steps guarantees a stronger, more durable connection, safeguarding the integrity of your piping system and reducing the risk of costly repairs.

