Locating the furnace vent in your home is a crucial step in understanding and maintaining your heating system. Whether you’re a new homeowner or simply unfamiliar with the intricacies of your heating infrastructure, identifying the furnace vent is essential for efficient operation and safety. The furnace vent serves as the gateway for exhaust gases to exit your home, ensuring that your heating system functions properly.

In this article, we will guide you through the process of how to find furnace vent, offering insights into common locations and potential variations in different homes.
By gaining a clear understanding of where your furnace vent is situated, you’ll be better equipped to monitor and maintain your heating system, fostering a warm and comfortable living environment. So, let’s embark on this informative journey to demystify the location of your furnace vent and enhance your home heating knowledge.
Importance of Locating Furnace Vents
Identifying the location of your furnace vents is not merely a matter of curiosity—it plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your heating system. Furnace vents, by design, channel harmful gases like carbon monoxide outside of your home, safeguarding the indoor air quality and preventing potential health risks.
Furthermore, knowing the precise location of these vents allows homeowners to keep them clear of obstructions, which could otherwise lead to the accumulation of hazardous gases or impair the system’s efficiency.
Regular monitoring and maintenance of the furnace vents also contribute to the overall energy efficiency of your home, reducing unnecessary heating costs and extending the lifespan of your heating system. Thus, understanding where your furnace vents are located is a critical step in responsible home maintenance.
Purpose of Furnace Vents in HVAC Systems
The purpose of furnace vents in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems is multifaceted, primarily designed to ensure the safety and efficiency of the heating process. These vents are responsible for safely expelling combustion byproducts, such as carbon monoxide, water vapor, and other gases that are produced during the operation of the furnace.
Without a properly functioning vent system, these hazardous gases could accumulate indoors, posing a serious threat to the occupants’ health. Additionally, furnace vents play a crucial role in maintaining the efficiency of the HVAC system.
By allowing for the proper expulsion of exhaust gases, they ensure that the furnace operates under optimal combustion conditions, thereby reducing fuel consumption and increasing energy efficiency. This not only contributes to a healthier living environment but also helps in lowering utility bills and reducing the environmental impact of heating homes.

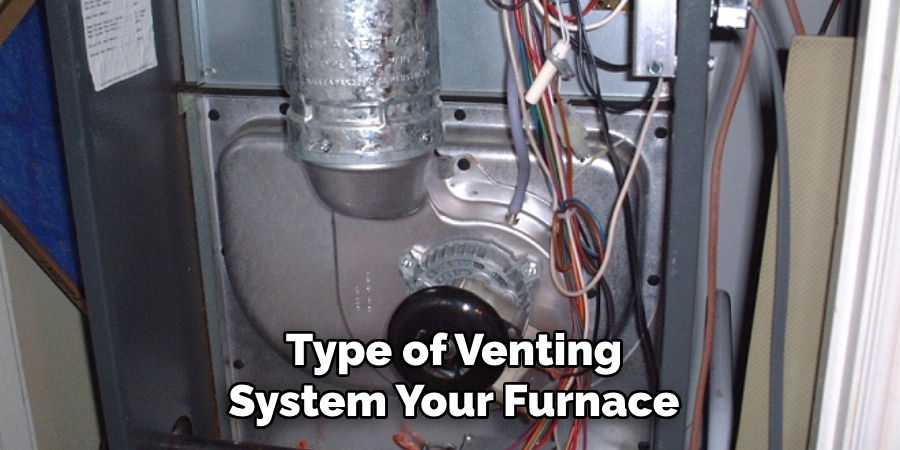
Different Types of Furnace Venting Systems
Furnace venting systems can vary greatly, depending on the type of heating equipment you have in your home and the age of the installation. Understanding the different types of venting systems is crucial for proper maintenance and safety. The most common types include:
- Natural Vent (Type B Vent): This is the traditional venting system found in older furnaces, where exhaust gases are expelled through a chimney or a vertical vent system by natural draft. This system relies on the natural rise of heated air to draw combustion gases out of the home.
- Direct Vent (Sealed Combustion): Modern and more energy-efficient, direct vent systems use two pipes for venting. One pipe brings outside air directly into the furnace for combustion, and the other expels exhaust gases outside. This system is sealed from the home’s interior, improving safety and efficiency by ensuring no indoor air is used for combustion and no combustion gases can enter the home.
- Power Vent: Similar to direct vent systems but with a key difference—a fan or blower is used to expel exhaust gases instead of relying on natural draft. This allows for more flexible installation since the vent pipes can be run horizontally, expanding placement options for the furnace.
- Condensing Vent: Utilized by high-efficiency condensing furnaces, these systems have a unique feature where the exhaust gases are cooled to a point where water vapor condenses into liquid, releasing additional heat energy. This system requires special venting resistant to corrosive condensate, typically made of PVC or a similar material.
Each type of venting system has its own set of requirements for installation, operation, and maintenance. Knowing which system your home utilizes is the first step in ensuring it operates safely and efficiently.
Typical Locations for Furnace Vents
Furnace vents can be found in a variety of locations within a home, largely depending on the type of venting system your furnace uses and the architectural design of your house. However, there are common places where you can start your search:
- Exterior Walls: Direct vent and power vent systems often terminate on an exterior wall of the home. Look for one or two pipes exiting the side of your house, close to the ground. These pipes are usually made of PVC in newer systems, but older systems might use metal.
- Roof: Natural vent systems, and some types of power vents, may terminate through the roof. Look for a chimney or vent stack protruding above the roofline. In homes with no chimney, there might be a pipe instead, which can be metal or PVC.
- Utility Rooms or Basements: The furnace itself is typically located in a utility room, basement, or a specific furnace room. From there, you can often trace the vent pipes as they exit the furnace and follow them to their termination point outside the home.
- Attic: In some homes, especially where there is no basement, the furnace may be located in the attic, and the vents may run up through the roof from there.
Being familiar with the type of furnace venting system your home employs will guide you in identifying the correct location of your vents. Always ensure that these vents are clear of obstructions and are inspected regularly to maintain your system’s efficiency and safety.
10 Methods How to Find Furnace Vent
1. Consult Home Blueprints or Manuals:
Reviewing your home’s blueprints or furnace manuals can provide valuable information about the location of the furnace vent. If you don’t have access to these documents, you can contact the builder or previous homeowners for assistance.
In addition to consulting blueprints or manuals, there are several other ways to locate your furnace vent. One option is to look for indicators such as a metal grate on the floor or wall near the furnace. This could indicate the location of the vent.
Another method is to follow the air flow. You can do this by placing your hand near potential vent locations and feeling for warm air coming from the vent. This method may be easier if you have multiple vents in your home.

Alternatively, you can also use a flashlight to inspect crawl spaces or attics for any signs of ductwork leading to the furnace vent. Be sure to exercise caution when entering these confined spaces.
2. Inspect Basement or Utility Room:
Furnace vents are often located in basements or utility rooms. Check these areas for vent pipes leading outside. It’s important to inspect these areas regularly to ensure that the vents are not blocked by debris or obstructions. This is especially important during the winter months when snow and ice can block exterior vents, causing dangerous carbon monoxide buildup.
Additionally, basements and utility rooms may also house other important components of your home’s HVAC system. These may include heat pumps, air handlers, and other mechanical equipment. It’s important to inspect these areas for any signs of damage, corrosion, or malfunction.
In addition to HVAC components, basements and utility rooms may also house water heaters, furnaces, and electrical panels. Make sure to regularly check on these appliances as well. Look for any signs of leaks, rust or wear and tear that could lead to potential safety hazards.
3. Look for Chimney or Vent Pipes on Roof:
The vent pipes connected to your furnace often extend through the roof. Examine your roof for any protruding pipes.
These pipes may be of various colors, such as metal or plastic. You will want to ensure that they are securely attached and not damaged in any way. If you notice any cracks or breaks, it is important to have them repaired as soon as possible.
In addition to checking for damage, make sure that there are no obstructions blocking the vent pipes. Leaves, branches, and debris can easily accumulate and block the flow of air. This can cause your furnace to work harder and less efficiently, leading to potential problems and increased energy costs.

4. Follow Ductwork:
Tracing the ductwork in your home can lead you to the furnace vent. Look for larger ducts that connect to the main heating system. These ducts are usually located near the ceiling in the basement or attic.
One important aspect of maintaining your ductwork is to ensure that it is properly sealed. Leaky ductwork can cause air to escape, reducing the efficiency of your heating system and increasing your energy bills. You should regularly check for any gaps or cracks in your ductwork and seal them with aluminum tape or mastic sealant.
In addition to sealing any leaks, another important step in maintaining your ductwork is to regularly clean it. Over time, dust, debris, and other pollutants can accumulate in your ducts, reducing the air quality in your home. This can be especially problematic for those with allergies or respiratory issues. To prevent this buildup, you should have your ducts professionally cleaned at least every 3 to 5 years.
5. Examine Exterior Walls:
Furnace vents can sometimes be located on exterior walls. Check for small pipes or vents near ground level. Look for signs of corrosion or damage on these vents. If you find any, be sure to address them in your report.
Exterior walls can give clues about the condition of a home’s structure and foundation. Cracks in the walls or gaps between bricks can indicate settling or shifting of the foundation. These issues should be noted and brought to the attention of the homeowner.

In addition to structural concerns, exterior walls can also reveal potential problems with insulation or moisture damage. Look for signs of water stains or mold growth on the walls, as well as any areas that feel noticeably colder than others. These could be indicators of poor insulation.
It is also important to check the overall condition of the exterior walls themselves. Look for peeling paint, rotting wood, or loose siding. These issues not only affect the appearance of the home, but they can also lead to more serious problems such as water damage and pest infestations.
6. Feel for Warm Air:
When the furnace is running, the air around the vent area may be warmer. Run your hand along walls or ceilings to sense temperature changes. Look for drafts or air movement around doors and windows. These could be signs of a poorly insulated home.
The purpose of insulation is to keep heat indoors during the winter months and to keep it out during summer months. Poor insulation can lead to high energy bills, as well as an uncomfortable living environment. In order to properly check if your home is properly insulated, it is important to do a thorough inspection of all areas where air can escape or enter.
One important area to check is the attic, as it is a common source of heat loss in homes. Insufficient insulation in the attic can result in warm air escaping and cold air entering, making your furnace work harder to maintain a comfortable temperature inside.
7. Check Near Gas Meter:
Furnace vents are often located near the gas meter. Inspect the area for vent pipes leading from the furnace. These pipes should be properly aligned and connected to the furnace. Make sure there are no gaps or damage in the pipes that can lead to gas leaks.

Frequently, homeowners may notice a rotten egg smell near their gas meter. This is a sign of a gas leak and should be taken seriously. If you suspect a gas leak, evacuate your home immediately and call your local utility company for assistance.
In addition to checking for gas leaks, it is important to regularly inspect the area around your gas meter for any signs of damage or wear. Extreme weather conditions, such as excessive heat or cold, can cause pipes and connections to become brittle and crack. If you notice any cracks or damage, it is important to call a professional immediately to address the issue.
8. Look for Vent Covers:
Some furnace vents may be covered with grates or caps. Search for these covers in areas where vents are expected. These can include stairwells, basements, and attics.
When looking for vent covers, it is important to thoroughly check all potential areas where vents may be located. This includes not only the main living areas of a house but also less commonly used spaces such as stairwells, basements, and attics.
In addition to checking these locations for existing vent covers, it is also important to inspect the condition of these covers. Over time, grates and caps can become damaged or rusted, which can affect their ability to properly cover and protect the furnace vents.
9. Use a Smoke Test:
On a cold day, light a candle and move it along walls. The flame may flicker or lean towards the vent, indicating airflow. If the flame remains steady, there may be an issue with your ventilation system.
A smoke test is a simple, yet effective way to check for proper ventilation in your home or building. It involves using a candle and observing how the flame behaves when held near walls or vents. This method can give you valuable information about the airflow in your space, helping you identify any potential issues that need to be addressed.
10. Seek Professional Help:
If you’re unable to locate the furnace vent, consider hiring a professional HVAC technician. They have the expertise and tools to identify vent locations. They will also be able to clean or repair any blocked or damaged vents.
In addition, a professional technician can also inspect your furnace for any potential issues and provide regular maintenance to ensure efficient and safe operation. It is recommended to have your furnace inspected at least once a year.

Moreover, if you’re experiencing frequent problems with your furnace or notice an increase in energy bills, it may be a sign of a bigger issue that requires professional attention. Don’t hesitate to seek help from a licensed HVAC technician to avoid any safety hazards and costly repairs in the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, locating furnace vents is crucial for maintaining efficient heating and proper ventilation within residential and commercial spaces. Understanding the various types of furnace venting systems and knowing where to look indoors and outdoors are essential steps in ensuring the functionality of HVAC systems.
By employing indoor and outdoor inspection techniques, using appropriate tools, and seeking professional assistance when needed, homeowners and building managers can effectively locate furnace vents and address any potential issues. Thanks for reading, and we hope this has given you some inspiration on how to find furnace vent!

