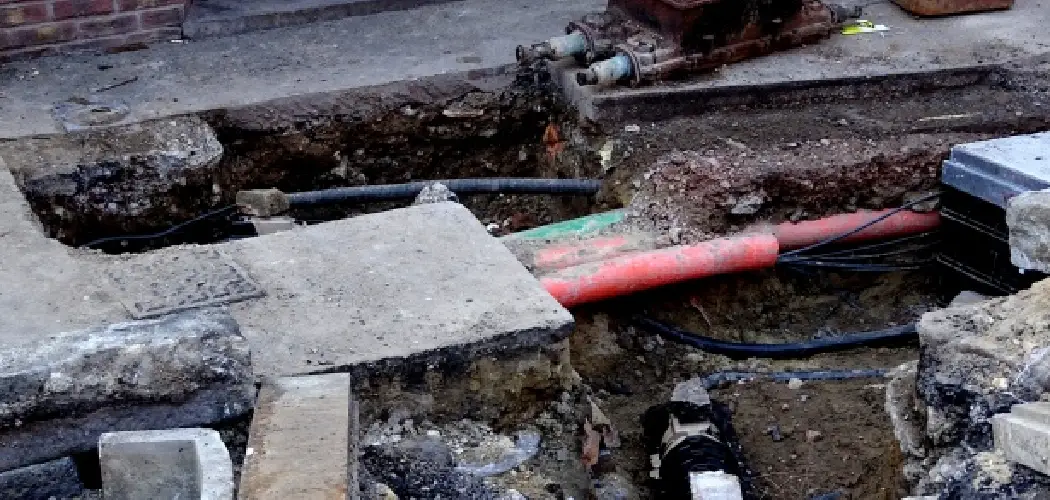
Properly insulating PEX (cross-linked polyethylene) pipes underground is crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your plumbing system, particularly in regions prone to freezing temperatures. PEX pipes, while highly durable and flexible, require adequate insulation to prevent heat loss and protect against the damaging effects of frost.
Understanding how to insulate PEX pipes underground involves selecting appropriate insulation materials, employing effective installation techniques, and adhering to local building codes and standards. Key steps in this process on how to insulate pex pipe underground, wrapping the PEX pipes with suitable insulating sleeves or foam, and ensuring the insulation is waterproof and weather-resistant. Additionally, taking measures to protect the pipes from sharp objects and potential ground shifts is vital.

By insulating PEX pipes properly, you not only enhance their performance and energy efficiency but also safeguard your plumbing system against costly repairs and potential disruptions, ensuring a reliable supply of water year-round.
Necessity to Insulate PEX Pipes Installed Underground
Insulating PEX pipes installed underground is not merely a recommendation but a necessity for several compelling reasons. First and foremost, in colder climates, uninsulated PEX pipes are vulnerable to freezing, which can lead to ruptures and extensive water damage. Frozen pipes not only disrupt the water supply but also pose a risk of flooding when the ice thaws. Furthermore, proper insulation aids in maintaining the temperature of the water being transported, which is particularly important for maintaining energy efficiency and reducing heating costs. Without insulation, the heat loss from hot water pipes can lead to increased energy consumption and higher utility bills.
Insulation also provides a protective barrier against physical damage from soil movement, rocks, and sharp objects that can compromise the integrity of the pipes. Lastly, adhering to insulation standards and building codes is often legally required to ensure the safety and reliability of residential and commercial plumbing systems. By insulating PEX pipes underground, homeowners and builders can prevent potential hazards, reduce maintenance costs, and promote sustainable energy use.
Importance of Protecting Underground PEX Pipes
The protection of underground PEX pipes goes beyond mere insulation; it ensures the overall integrity and reliability of your plumbing system. One crucial aspect of protecting these pipes is shielding them from physical damage caused by ground movement, soil pressure, and the intrusion of roots from nearby plants. These elements can exert stress on the PEX pipes, leading to potential cracks and leaks which could compromise the plumbing infrastructure. Additionally, protecting PEX pipes from potential contamination is vital.

Chemicals and pollutants present in the soil can degrade pipe material over time, risking the safety and purity of the water supply. By installing protective barriers and using robust, resistant materials during installation, you can prevent these harmful effects and extend the life span of your plumbing system. Furthermore, proper protection measures ensure compliance with local building codes and standards, guarding against potential legal and financial repercussions. Ultimately, taking proactive steps to protect underground PEX pipes not only maintains the functionality and efficiency of the plumbing system but also offers peace of mind, knowing that the infrastructure is secure and reliable for years to come.
Understanding the Need for Insulating
To fully comprehend the necessity for insulating PEX pipes installed underground, it is important to examine the underlying factors that drive this requirement. The primary reason is the prevention of freezing in cold weather conditions. When temperatures drop, water within uninsulated pipes can freeze, leading to blockages and potential pipe bursts. These ruptures can result in significant property damage and costly repairs. Insulating PEX pipes helps maintain a stable temperature, ensuring a continuous flow of water even during severe weather.

Aside from freeze protection, insulation enhances the energy efficiency of water heating systems by minimizing heat loss as hot water travels through the pipes. This reduction in heat loss translates directly into lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills, making insulation a cost-effective investment over time. Furthermore, insulation serves as a buffer against physical impacts from soil shifts, rocks, and other underground hazards, preserving the structural integrity of the pipes.
Adhering to local building codes that mandate the insulation of PEX pipes is not just a regulatory formality; it is a critical measure to ensure the long-term reliability and safety of the plumbing system. Overall, insulating PEX pipes underground is essential for maintaining operational efficiency, preventing damage, and promoting sustainable, energy-efficient practices in residential and commercial plumbing.
Risks Associated with Underground PEX Pipes
Despite the advantages of using PEX pipes for underground plumbing, there are several risks associated with their installation and use. One significant risk is the susceptibility to damage from soil movement and shifting. Over time, natural soil compaction, erosion, or seismic activity can place stress on the pipes, leading to cracks, leaks, or even breaks. Additionally, the pressure exerted by heavy vehicles or construction equipment on the surface can contribute to pipe deformation or damage if the pipes are not adequately protected.
Another substantial risk involves chemical interactions. Soil composition varies widely, and in some areas, the presence of harsh chemicals, solvents, or corrosive agents can gradually degrade PEX material. This chemical interaction can compromise the integrity of the pipes, raising concerns about contamination of the water supply and potential health risks.

Furthermore, there is the risk of temperature fluctuations. In regions with extreme temperature variations, both the external environment and the temperature of the transported water can affect the pipes. Rapid expansion and contraction due to temperature changes can weaken the PEX material, potentially leading to fractures or leaks.
The threat from plant roots should also not be underestimated. Roots from nearby trees or shrubs can infiltrate the space around the pipes, exerting pressure that may cause damage. As roots grow and expand, they can wrap around and crush the pipes or penetrate weak points, leading to costly repairs.
Lastly, proper installation is crucial; improper installation techniques or the use of substandard materials can leave PEX pipes vulnerable to all the aforementioned risks. Ensuring that pipes are installed according to best practices and adhering to local building codes can mitigate many of these risks, ensuring the long-term reliability of the plumbing system. Don’t forget, failure to properly address these risks can result in significant maintenance costs and potentially severe disruptions to water supply.
Benefits of Insulating Underground PEX Pipes
Insulating underground PEX pipes offers several noteworthy benefits that contribute to the efficiency and longevity of your plumbing system. Firstly, insulation provides a critical barrier against temperature extremes. By maintaining a more stable internal pipe temperature, insulation prevents the water inside from freezing during the winter or overheating in the summer, thus ensuring a consistent and reliable water supply year-round. This temperature regulation helps to avoid costly repairs associated with burst pipes due to freezing.
Another significant advantage is the enhancement of energy efficiency. Insulated PEX pipes reduce heat loss when transporting hot water, leading to a more efficient water heating system. This means lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills, as less energy is required to maintain the desired water temperature. Over time, this translates into considerable cost savings and a smaller environmental footprint.

Insulation also acts as a safeguard against physical damage. It protects the pipes from the stresses of soil pressure, potential impacts from rocks, and other underground hazards. This fortification preserves the structural integrity of the PEX pipes, reducing the likelihood of leaks or breaks that can result in water wastage and extensive repair costs.
Moreover, proper insulation helps comply with local building codes and standards, which often mandate insulation for underground PEX installations. This compliance not only ensures adherence to legal requirements but also promotes best practices in plumbing, instilling confidence in the durability and performance of the system.
In summary, insulating underground PEX pipes is a proactive measure that offers multiple benefits, including preventing freeze damage, enhancing energy efficiency, protecting against physical impacts, and ensuring code compliance. These advantages collectively contribute to a more reliable, cost-effective, and sustainable plumbing infrastructure.
10 Methods How to Insulate Pex Pipe Underground
1. Assess the Installation Area
Before starting the insulation process, it’s essential to thoroughly assess the installation area. Understanding the soil type, local climate conditions, and the depth at which the pipes will be buried helps determine the appropriate insulation materials and techniques. For instance, regions with colder climates will require more robust insulation solutions to prevent freezing. By conducting a thorough assessment, you can tailor your insulation approach to meet the specific needs of your project, ensuring maximum efficiency and protection for the PEX pipes.
2. Select Suitable Insulation Material
Choosing the right insulation material is critical for effectively insulating PEX pipes underground. Common materials include foam pipe insulation, fiberglass pipe wrap, and polyethylene foam tubing. Each material has its own advantages: foam pipe insulation is flexible and easy to install, fiberglass offers excellent thermal resistance, and polyethylene foam tubing is resistant to moisture.

Select an insulation material that is suitable for underground use, offers high thermal resistance (R-value), and is compatible with PEX pipes. Ensure the material can withstand soil pressure and moisture to maintain its insulating properties over time.
3. Dig an Appropriately Sized Trench
Digging the trench correctly is a crucial step in the insulation process. The trench should be deep enough to accommodate the PEX pipes and the insulation material, typically at least 12 to 24 inches below the frost line to prevent freezing. Ensure the trench is wide enough to allow for the installation of the insulation around the pipes without compressing it. The bottom of the trench should be smooth and free of sharp objects that could damage the pipes or insulation. Proper trench depth and width are vital to ensuring the insulation’s effectiveness and the long-term integrity of the pipes.
4. Lay a Sand or Gravel Base
Creating a stable base in the trench helps protect the PEX pipes and insulation from ground movement and potential damage. Lay a 2 to 3-inch layer of sand or gravel at the bottom of the trench to provide a smooth, stable surface. This base material acts as a cushion, reducing the risk of punctures or abrasions to the pipes and insulation. Sand or gravel also promotes proper drainage, preventing water from accumulating around the pipes, which can lead to freezing and other issues. A stable base is essential for maintaining the integrity of the PEX pipes and insulation over time.
5. Install the PEX Pipes
Carefully lay the PEX pipes in the trench, ensuring they are properly aligned and positioned. Avoid bending or kinking the pipes, as this can affect their performance and durability. If installing multiple pipes, ensure they are spaced adequately to allow for proper insulation around each pipe. Secure the pipes in place using stakes or other supports to prevent movement during the insulation process. Properly installed PEX pipes provide a solid foundation for effective insulation and long-term performance.
6. Wrap the Pipes with Insulation Material
Once the PEX pipes are in place, wrap them with the selected insulation material. For foam pipe insulation, cut the insulation to the appropriate length and secure it around the pipes using tape or zip ties. Ensure the insulation material covers the entire length of the pipes, including joints and bends, to provide comprehensive protection. If using fiberglass wrap, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper application, ensuring a snug fit around the pipes. Wrapping the pipes thoroughly with insulation material helps prevent heat loss and protects against freezing temperatures.
7. Seal Joints and Seams
Sealing joints and seams in the insulation is crucial to prevent heat loss and ensure the effectiveness of the insulation. Use insulation tape or a high-quality sealant to secure all joints and seams, ensuring a tight, watertight seal. This prevents moisture from entering the insulation and compromising its thermal properties. Pay special attention to areas where pipes bend or connect, as these spots are more susceptible to gaps. Properly sealed joints and seams help maintain the integrity of the insulation and ensure consistent protection for the PEX pipes.

8. Add an Extra Layer of Protection
In areas with particularly harsh climates or where additional protection is desired, consider adding an extra layer of insulation or a protective covering. This could include an additional wrap of foam insulation, a layer of heavy-duty polyethylene sheeting, or a PVC casing. These extra layers provide additional thermal resistance and physical protection against soil pressure and potential damage from roots or sharp objects. An extra layer of protection enhances the durability and performance of the insulation, ensuring the PEX pipes remain protected under extreme conditions.
9. Backfill the Trench Carefully
After the insulation is in place, carefully backfill the trench with the excavated soil. Start by adding a layer of sand or gravel to provide additional support and drainage around the insulated pipes. Gradually add soil in layers, compacting each layer gently to avoid damaging the insulation or pipes. Ensure the soil is evenly distributed to prevent any voids or air pockets that could compromise the insulation. Proper backfilling helps maintain the insulation’s effectiveness and provides stability to the PEX pipes, preventing movement and potential damage.
10. Monitor and Maintain the Insulation
Regular monitoring and maintenance are essential to ensure the long-term effectiveness of the insulation. Periodically inspect the area for signs of ground movement, erosion, or water accumulation, which could impact the insulation and PEX pipes. If any issues are detected, address them promptly to prevent further damage. In colder climates, consider adding additional insulation or protective measures as needed to account for changes in weather patterns. Regular maintenance helps ensure the insulation continues to provide effective protection, extending the lifespan of the PEX pipes and maintaining efficient performance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Inadequate Trench Depth: One of the most common errors is not digging the trench deep enough. Failing to dig below the frost line can result in freezing pipes, which can lead to punctures or breaks. Ensure your trench is at least 12 to 24 inches below the frost line for proper protection.
- Poor Insulation Material Choice: Not all insulation materials are created equal. Using substandard or inappropriate materials can compromise the insulation’s effectiveness. Always choose high-quality, weather-resistant insulation designed specifically for underground use.
- Inconsistent Insulation Coverage: Leaving gaps or not fully covering the pipes with insulation material can lead to cold spots, reducing the overall efficiency of the insulation. Make sure every inch of the PEX pipes, including joints and bends, is thoroughly insulated.
- Improper Pipe Alignment: Misaligned pipes can cause kinks, reducing water flow and increasing the risk of leaks. Ensure the PEX pipes are laid straight and evenly without sharp bends or distortions.
Conclusion
Properly insulating buried PEX pipes is vital for ensuring their longevity and performance, particularly in climates subject to freezing temperatures. By choosing the right insulation materials, digging an appropriately sized trench, creating a stable base, and carefully installing and wrapping the pipes, you can significantly reduce the risk of heat loss and freezing. Sealing joints and seams and adding extra layers of protection in harsh climates further enhance the effectiveness of the insulation.
Finally, careful backfilling and regular monitoring and maintenance help maintain the integrity of the insulation and the PEX pipes, ensuring they continue to function efficiently over time. Thanks for reading, and we hope this has given you some inspiration on how to insulate pex pipe underground!

