A properly functioning igniter in a gas furnace is crucial for ensuring that the furnace ignites efficiently and operates safely. Without a reliable igniter, homeowners may face a series of challenges, including the furnace failing to ignite, leading to an uncomfortable and cold environment within the home. More critically, a faulty igniter can result in a buildup of gas, posing potential safety hazards, including the risk of gas leaks or explosions.

Therefore, understanding how to test igniter on gas furnace is an essential piece of knowledge for maintaining the safety and efficiency of your heating system. However, dealing with gas appliances requires a high degree of caution and adherence to safety precautions to prevent accidents.
Suppose at any point you feel unsure or uncomfortable performing any tests on your furnace. In that case, it is strongly recommended that you consult a qualified HVAC professional to assess and service your furnace. Their expertise ensures that your furnace continues to operate safely and efficiently, reducing the risk of emergency repairs during cold weather.
The Role of the Igniter in Gas Furnaces
The ignition sequence in a gas furnace is a carefully timed process that ensures the efficient and safe production of heat. It begins when the thermostat detects a need for warmth and sends a signal to the furnace. This triggers the gas valve to open, allowing natural gas to flow into the combustion chamber.
At this critical juncture, the igniter comes into play with its paramount task—initiating the combustion process. Depending on the type of system, this involves either heating up to glow red hot or generating a spark. When the gas encounters the igniter’s heat or spark, it ignites, creating the flames that heat the exchanger. Subsequently, the furnace’s blower distributes the resultant warmth throughout the home.
There are two principal types of igniters found in modern gas furnaces, each with its unique operation method. The first, known as a glow bar igniter, functions by electrically heating up to a high temperature, glowing red, and igniting the gas. This type of igniter is widely used for its reliability and the smooth, consistent ignition process it provides. On the other hand, the spark igniter operates differently by generating a high-voltage spark to ignite the gas directly.
This type offers a different set of advantages, including durability and efficiency in certain furnace designs. Both types are critical in the safe and effective operation of gas furnaces, ensuring that heat is produced whenever needed without delay.
Signs of a Faulty Igniter
Identifying a problem with the furnace igniter early can save homeowners from more significant issues down the line. You might suspect a faulty igniter if you encounter the following signs:
- The furnace fails to ignite on multiple attempts, producing no heat.
- For those with pilot light furnaces, the pilot light refuses to stay lit, indicating an ignition issue.
- If you notice a burning smell or unusual noises during ignition attempts, it might be a sign of a faulty igniter struggling to perform its task.
- An increase in gas bills could suggest inefficient furnace operation, often due to a malfunctioning igniter or related components that do not initiate the combustion process efficiently.
Importance of Identifying the Issue
While a faulty igniter is a common culprit behind ignition problems, it’s crucial to rule out other potential causes before proceeding with any tests. Issues with the thermostat or gas supply, among others, can also lead to similar problems, and discerning the exact cause is essential for effective troubleshooting.
Identifying whether the igniter is at fault allows homeowners to take precise measures, ensuring their furnace operates safely and efficiently. This step is vital in preventing unnecessary repairs or replacements and in maintaining the furnace’s overall health.
Safety Precautions Before Testing
Before attempting to test the igniter on your gas furnace, safety must be paramount. This process involves dealing with electrical components and flammable gas, both of which present substantial risks if not handled correctly. To mitigate these risks and ensure a safe testing environment, follow these essential safety precautions.
Turning Off the Furnace

First and foremost, turn off your furnace at the thermostat. This step prevents the furnace from attempting to activate while you are working on it. Once the thermostat is set to off, proceed to switch off the power supply to the furnace at the breaker.
This action ensures no electrical power is running to the furnace, eliminating the risk of electrical shocks. Confirming that the power is indeed off before you begin any work on your furnace is important.
Ensuring a Well-Ventilated Area
By their nature, gas furnaces involve the use of natural gas—a substance that can be harmful if inhaled in large quantities. Therefore, conducting any work on your gas furnace in a well-ventilated area is crucial. This precaution helps in dissipating any gas that might be released accidentally during the testing process, avoiding potential health hazards.
If you’re working in a confined space, consider using a fan to aid in ventilation or work in short intervals to allow for regular airing out of the space.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Wearing the right protective gear can significantly reduce the risk of injury when working on your furnace. Gloves protect your hands from sharp edges and hot surfaces, while safety glasses guard against dust, debris, and any unexpected sparks. Opting for flame-resistant clothing can also provide an additional layer of safety, especially when dealing with components that may interact with gas or flames.
Shutting Off the Gas Supply
If the testing process requires access to parts of the furnace where gas flow is involved, shutting off the gas supply valve to the furnace might be necessary. This step ensures that no gas flows into the furnace while you are working on it, thereby preventing potential gas leaks or unintentional ignition.

However, if you’re unsure how to properly shut off the gas supply or if doing so makes you uncomfortable, it’s wise to consult a professional HVAC technician. A qualified professional can either perform the task for you or guide you through the process safely.
Taking these safety precautions seriously ensures your well-being and helps prevent damage to your furnace. Remember, safety first—never hesitate to seek professional help if you’re unsure about any part of the testing process.
Tools and Resources Needed for Testing
Testing your furnace’s igniter for faults requires specific tools and resources to ensure accuracy and safety during the diagnosis. Key tools include:
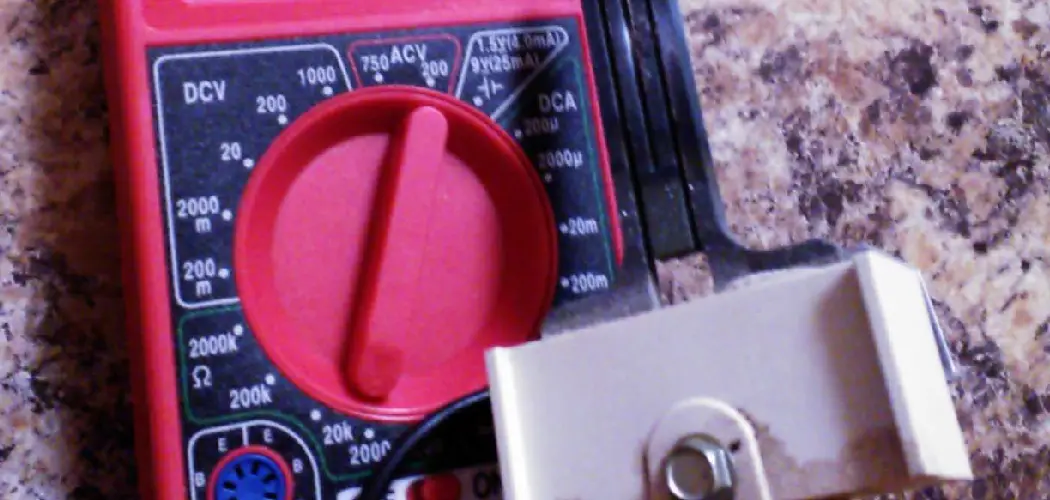
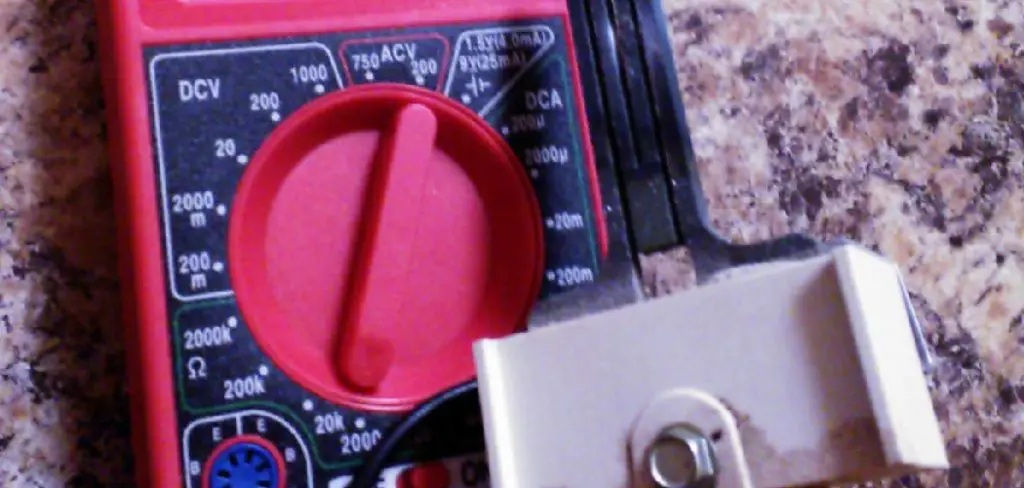
- Multimeter: A crucial tool for this task is a multimeter that measures electrical properties such as continuity, voltage, and resistance. The continuity and voltage functions are most relevant for testing an igniter. The continuity test checks if there is a continuous electrical path present—an essential factor for an igniter’s operation. Meanwhile, voltage measurements can help determine if the igniter is receiving the necessary power to function.
- Screwdriver: This tool is necessary for accessing the furnace’s internal components. Most furnaces are secured with screws, and a screwdriver will allow you to open the panel safely and efficiently.
- Flashlight: Good lighting is essential, especially when working on components located in dark or hard-to-reach areas inside the furnace. A flashlight can help you see clearly, ensuring accuracy while testing and evaluating different parts.
Before beginning any testing, it’s recommended to consult your furnace’s manual or the manufacturer’s website for specific instructions related to your model. These resources can provide crucial information on the location of components, the type of igniter your furnace uses, and any specific precautions to take during the testing process. They often include troubleshooting steps that are tailored to your furnace model, offering a valuable guide through the diagnosis.
Obtaining a service manual specific to your furnace model can be incredibly helpful for those seeking more in-depth information or if your furnace manual is not readily available.

Service manuals offer comprehensive details on all aspects of the furnace, from installation and operation to troubleshooting and repair. These manuals can often be found online through the manufacturer’s website or by contacting their customer service. In some cases, a nominal fee may be required, but the investment is worthwhile for the wealth of information provided.
Having the right tools and resources at hand simplifies the process of testing your furnace’s igniter and streamlines troubleshooting. By understanding the function of each tool and utilizing available manuals and guides, homeowners can safely and effectively identify issues with their furnaces, ensuring continued comfort and safety in their homes.
Visually Inspecting the Igniter
Visually inspecting the igniter is a crucial step before proceeding with electrical testing. An initial visual assessment can reveal obvious signs of damage or wear that could indicate potential problems. Look closely for any cracks, signs of burning or corrosion, and loose connections; these issues can compromise the igniter’s functionality and may even pose safety risks.
Cracks in the ceramic could lead to a failure in sparking, while corrosion and burning signs could indicate problems with the electrical system or gas flow, impacting the igniter’s performance. Loose connections, too, might prevent the igniter from receiving the necessary power to operate correctly.
If any visible damage is detected during the inspection, it’s advisable to replace the damaged igniter before attempting further troubleshooting or electrical testing. Operating a furnace with a damaged igniter can lead to inefficient heating or, worse, a safety hazard.
Given the intricate nature of furnace systems and the importance of precise installation, consulting a professional HVAC technician for igniter replacement and further troubleshooting is recommended. This approach ensures that any underlying issues are properly addressed, maintaining the safety and efficiency of your heating system.

How to Test Igniter on Gas Furnace: Testing a Glow Bar Igniter
A. Testing for Continuity
To effectively test a glow bar igniter for continuity, begin by ensuring the furnace power is completely off as a safety precaution. Using a multimeter, set it to the continuity setting, normally represented by a horseshoe symbol. This step is crucial for preparing to test the igniter’s electrical flow. With the power off, carefully disconnect the wires attached to the igniter terminals, ensuring that the circuit is open for testing.
Place one multimeter probe on each terminal of the igniter. A properly functioning igniter will cause the multimeter to emit a continuous beep, indicating a continuous electrical path exists through the igniter—signifying it is in good condition. Conversely, the absence of a beep sound suggests there is a break in the circuit, pointing toward a faulty igniter. This simple but effective test can quickly determine the health of the igniter, helping diagnose potential heating problems.
B. Testing for Resistance
An alternative to continuity testing for a glow bar igniter is to measure its resistance. This method may offer a more nuanced insight into the igniter’s condition for those who prefer a detailed analysis. To proceed, first, ensure the furnace power is off and disconnect the igniter wires. Set the multimeter to the ohms setting, often symbolized by the omega (Ω) symbol.
Similar to the continuity test, you will need to touch the multimeter probes to each of the igniter’s terminals. A reading that falls within the manufacturer’s specified range indicates a functional igniter. It’s essential to refer to the furnace’s manual or manufacturer’s online resources for exact resistance specifications.
A resistance measurement significantly outside of this range or a zero reading denotes a fault in the igniter. This testing method is slightly more intricate but critically assesses whether the igniter operates within its expected functional parameters, thus ensuring the efficiency and safety of the furnace system.

How to Test Igniter on Gas Furnace: Testing a Spark Igniter
Testing a spark igniter is a more nuanced and sometimes demanding process than testing a glow bar igniter. It often requires observation during the furnace’s operation to gauge performance accurately. This section will guide homeowners through a structured approach to assessing the functionality of their spark igniter, ensuring the safety and efficiency of their heating system.
A. Observational Test
For this diagnostic method, begin by ensuring the furnace power is switched back on. Adjust the thermostat to the “heat” setting to initiate an ignition cycle, making sure your gas supply is fully operational. During this process, closely observe the igniter tip for any visible spark when the furnace attempts to ignite.
The presence of a spark at the igniter tip usually signifies a functioning igniter, carrying out its role in igniting the furnace’s gas correctly. Conversely, the absence of a spark may point towards an underlying issue within the igniter itself or possibly within the related electrical connections or gas delivery mechanisms. Identifying whether a spark occurs is crucial as it directly influences the ability of the furnace to generate heat effectively.
B. Multimeter Test (if comfortable)
This method is recommended for those with a higher level of comfort in handling electrical testing tools and understanding furnace electrical systems. To proceed, ensure your multimeter is set to the AC voltage (VAC) setting. Consult your furnace’s manual or manufacturer’s guidance for the precise locations of wire terminals near the spark igniter module to connect your multimeter probes accurately.
Once set up, carefully observe the multimeter’s reading while your furnace attempts an ignition cycle. A voltage reading during the process of spark generation is indicative of a functioning igniter circuit, affirming that the necessary electric charge is being delivered to produce a spark.
On the other hand, the absence of a voltage reading during this critical period might suggest a malfunction within the igniter module or potential issues in the connecting wiring. This advanced diagnostic tool offers a deeper insight into the electrical aspects of the spark igniter’s operation, providing a more comprehensive overview of the system’s health.

Interpreting Test Results and Next Steps
Upon conducting the tests detailed in the previous sections for both glow bars and spark igniters, homeowners will have gathered valuable diagnostic information on their furnace igniters’ condition. Test results fall into two primary categories: indicating either functional integrity or suggesting a fault.
For glow bar igniters, a continuous beep during the continuity test or a resistance measurement within the manufacturer’s specified range points to a healthy igniter. In contrast, the absence of a beep or an out-of-range resistance value signals potential issues.
Similarly, for spark igniters, observing a visible spark during the operational test or witnessing the expected voltage reading during the multimeter test denotes proper function. At the same time, the absence of these indicators points towards a malfunction.
It’s crucial to understand that a faulty igniter, while a common issue, is just one of several potential problems that could affect furnace operation. Other issues might include problems with the furnace’s control board, safety switches, thermostats, or even the gas supply system. Consequently, accurately diagnosing and resolving furnace problems often requires a holistic understanding of the system.
If the tests suggest a faulty igniter, or if homeowners are uncomfortable with interpreting the results or proceeding with further troubleshooting, consulting a qualified HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) professional is highly recommended. An experienced technician can provide a comprehensive diagnosis, confirming whether the issue lies solely with the igniter or elsewhere in the system.
In terms of repair options, if the igniter is determined to be at fault, replacement is typically straightforward but must be executed with precision to ensure proper alignment and functionality. The repair might involve replacing only the igniter itself or, depending on the diagnosis, the entire igniter module. The choice between these options depends on the specific issues identified and the design of the furnace system.
It’s also worth noting that even when a homeowner is capable of replacing the igniter, HVAC systems are complex and interdependent, meaning that incorrectly diagnosing problems or improperly executing repairs could inadvertently create additional issues.
In summary, while the initial diagnosis of igniter problems is within the reach of many homeowners equipped with a multimeter and a basic understanding of their furnace system, identifying and correcting the root cause of furnace malfunctions often necessitates the expertise of a professional.
Following the guidelines for testing and interpreting test results is a key step in furnace maintenance, but recognizing when to call in a professional can save time, ensure safety, and guarantee the long-term reliability of your heating system.
Safety Reminders and Conclusion
Safety should be the paramount concern at every stage of learning how to test igniter on gas furnace and conducting any associated repairs. Before initiating any diagnostic tests or repairs, turning off the power to the furnace and the gas supply is critical to mitigate risks of electrical shock or gas leakage. This precaution ensures a safe environment for you to work in.
Recognizing when a task exceeds your comfort level or technical proficiency is also crucial. In such cases, seeking the assistance of a qualified HVAC professional is not only advisable but essential. These experts have the knowledge and tools to safely diagnose and repair furnace issues, ensuring your heating system’s efficiency and safety.
A properly functioning igniter is essential for efficient and reliable furnace operation. Faulty igniters can lead to unsuccessful ignition cycles, resulting in poor heating performance or potentially hazardous conditions. Regular furnace maintenance by a certified professional can help prevent igniter and other furnace-related issues before they escalate, ensuring your system operates safely and effectively.

In summary, understanding how to test the igniter on a gas furnace and when to enlist professional help is vital for maintaining a safe and efficient heating system. Regularly scheduled professional maintenance is the best strategy to prevent future problems, safeguarding the comfort and safety of your home.

