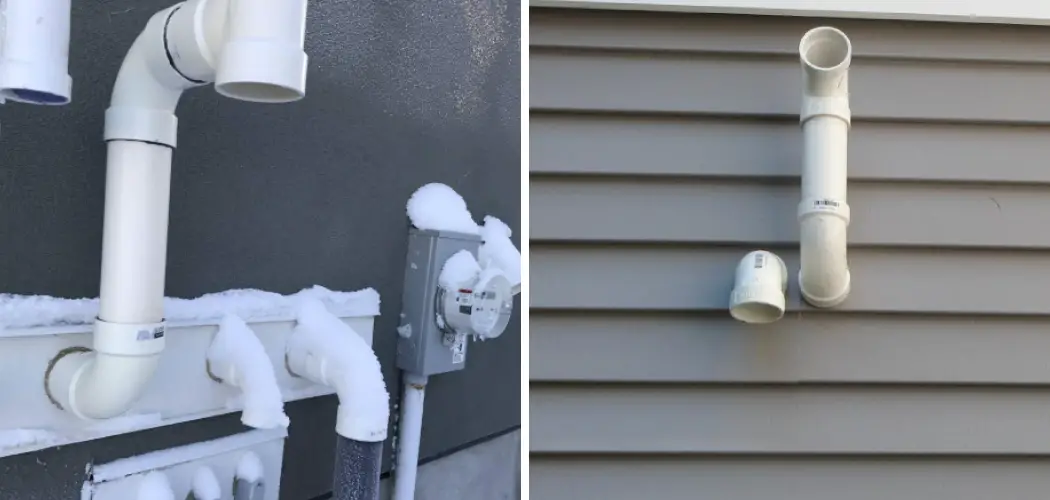
Thawing frozen furnace exhaust pipes is crucial for maintaining a safe and efficient home heating system during the cold weather months. Frozen pipes can prevent the escape of harmful gases, posing serious health risks to inhabitants and potentially causing significant damage to the property. Learning how to thaw frozen furnace exhaust pipe is essential for homeowners in colder climates to prevent these dangers.
Frozen exhaust pipes can lead to a buildup of carbon monoxide within the home, a colorless, odorless gas that can be deadly. Additionally, the pressure from trapped gases can cause the furnace to malfunction or even result in the exhaust pipe bursting, leading to costly repairs and potential safety hazards for residents.
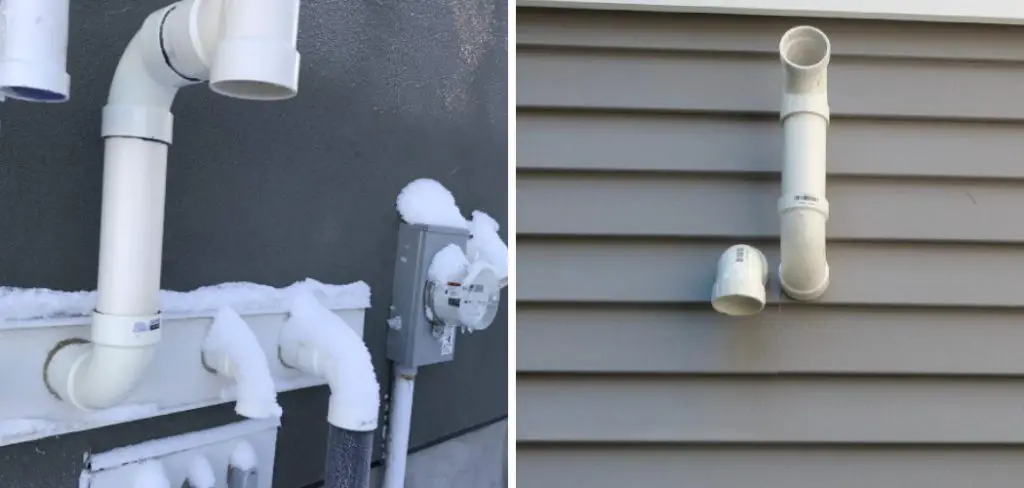

This article aims to provide homeowners with a comprehensive guide on how to thaw frozen furnace exhaust pipes safely and effectively. Covering various methods and techniques, the guide seeks to empower readers with the knowledge to address this common winter issue while emphasizing the importance of safety and prevention.
Understanding Frozen Furnace Exhaust Pipes
A. Causes of Freezing (e.g., Cold Weather, Condensation)
The primary cause of a frozen furnace exhaust pipe is the presence of extremely cold weather, leading to the rapid cooling of moisture within the pipe, which then freezes. This situation is exacerbated by the presence of condensation, which occurs when the warm, moist air from the furnace meets the cold pipe exterior. Factors like sudden drops in temperature, high humidity levels, and inadequate insulation can all contribute to the freezing of furnace exhaust pipes.
B. Risks and Consequences of Blocked Exhaust Pipes
Frozen furnace exhaust pipes pose significant risks as they block the escape of hazardous gases, such as carbon monoxide, back into the home. This can lead to potentially life-threatening situations for inhabitants due to carbon monoxide poisoning. Furthermore, the blockage increases internal pressure within the furnace system, which can cause it to malfunction, shut down, or, in extreme cases, lead to cracks or bursts in the piping, thus resulting in expensive repairs and safety hazards.

C. Signs of a Frozen Exhaust Pipe
Identifying a frozen exhaust pipe early is crucial to preventing risks. Signs include the furnace failing to start or repeatedly shutting down shortly after starting, strange noises emanating from the furnace area, and the presence of an unusual smell indicative of gases being forced back into the house. Additionally, visible ice formation on the exterior of the exhaust pipe or water dripping from it during colder months can also indicate freezing issues.
Safety Precautions
Ensuring safety is paramount when addressing a frozen furnace exhaust pipe. The procedure involves certain risks, primarily from exposure to extreme temperatures and potential contact with harmful gases. Therefore, adopting appropriate safety measures is essential to prevent accidents and health hazards.
A. Importance of Safety Gear (e.g., Gloves, Safety Glasses)
Before attempting to thaw a frozen exhaust pipe, it is crucial to wear the appropriate safety gear. Protective gloves are necessary to prevent frostbite and other injuries related to the cold or from handling tools and materials. Safety glasses are also recommended to protect the eyes from possible debris or chemical splashes, especially if using substances to melt the ice. These pieces of safety equipment provide a basic level of protection and are the first step in ensuring the individual’s safety during the thawing process.
B. Turning Off the Furnace to Prevent Further Damage
Turning off the furnace before beginning the thawing procedure reduces the risk of damage to the furnace and exhaust system. This action prevents the furnace from forcing more gas through the blocked exhaust, which could exacerbate the situation by building up more pressure or by causing more water vapor to freeze. Turning off the furnace also lowers the risk of carbon monoxide buildup within the premises, creating a safer environment for the thawing process.
C. Ensuring Proper Ventilation During Thawing Process
Maintaining adequate ventilation is critical when working to thaw a frozen furnace exhaust pipe. Proper airflow helps to dissipate any gases that may be released during the thawing process, particularly if the blockage has caused a buildup of harmful gases like carbon monoxide. Opening windows and doors near the work area or using fans to enhance air circulation minimizes the risk of gas accumulation and exposure, safeguarding the health of anyone involved in or near the thawing process.

Assessing the Situation
Before attempting any thawing measures, a thorough assessment of the situation is crucial to ensure an effective and safe resolution. This involves determining the exact location of the freeze, inspecting the exhaust pipe for ice build-up and other blockages, and evaluating the severity of the freeze. Proper assessment not only aids in selecting the most appropriate thawing method but also helps avoid potential damage to the furnace system.
A. Locating the Frozen Section of the Exhaust Pipe
The first step in addressing a frozen furnace exhaust pipe is to locate the frozen section accurately. Typically, the most susceptible areas to freezing are those exposed to the external environment or where there is a significant drop in temperature. Check the exterior part of the exhaust pipe, especially where it exits the house, as this is a common freeze point. Look for visible signs of ice or frost on the pipe’s exterior. In some instances, the frozen section might be within an accessible part of the attic or crawl space where the pipe is less insulated.
B. Inspecting for Ice Build-Up and Blockages
Once the frozen section has been located, a detailed inspection will be conducted for ice build-up and blockages. It’s important to note that not all blockages will be visible from the exterior, as ice can form on the interior walls of the exhaust pipe, narrowing its diameter and restricting gas flow. Use a flashlight to inspect the inside of the pipe as much as possible. Signs of ice include frost buildup around the seam or joints of the pipe and cold spots along the pipe’s length.

C. Determining Severity of the Freeze
Determining the severity of the freeze is vital for deciding the appropriate thawing technique. Assess the thickness of the ice, the length of the pipe affected, and whether there are multiple freeze points. Minor freezes, where ice is thin and localized, may be resolved with simpler measures, such as using a hairdryer or heat gun. However, more severe freezes, characterized by thick ice build-up over a large section of the pipe, might require more intensive thawing methods and potentially professional intervention. If the pipe is significantly frozen, there is also an increased risk of damage to the pipe itself and the surrounding structure, necessitating a careful approach to thawing.
How to Thaw Frozen Furnace Exhaust Pipe: Thawing Methods
Effectively thawing a frozen furnace exhaust pipe requires a careful and measured approach to prevent damage to the pipe and ensure personal safety. Here are some recommended methods:
A. Using Heat Sources (e.g., Hair Dryer, Heat Gun)
One of the most common and safest methods to thaw a frozen pipe is by using heat sources such as a hair dryer or a heat gun. When using these devices, start by setting them on the lowest heat setting to warm the pipe gradually and avoid thermal shock, which could damage the pipe. Move the device slowly back and forth along the frozen section, ensuring that heat is distributed evenly. It’s important not to concentrate heat on one area for too long to prevent melting or deforming the pipe. This method is suitable for minor to moderate freezes and can be effective in slowly melting the ice without causing damage.
B. Applying Warm Water or Towels
Another method involves applying warm water or hot towels to the frozen section of the exhaust pipe. For warm water, you can use a spray bottle to gently apply warm water to the frozen area. This method requires patience as it may need to be repeated several times to effectively thaw the ice. Alternatively, soaking towels in hot water and then wrapping them around the pipe can also help in transferring heat directly to the ice. It’s crucial to ensure that the water is not too hot to avoid any sudden temperature changes that could harm the pipe. This method is particularly useful for accessible sections of the pipe where direct application is feasible.
C. Utilizing Safe Chemical Solutions
In some cases, applying safe chemical solutions that are designed to melt ice can be an option. Products like calcium chloride or magnesium chloride can effectively melt ice without the need for direct heat. These chemicals can be spread around the affected area of the pipe but should be used cautiously. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and wearing protective gloves and safety glasses when handling these chemicals is important. Additionally, one should consider the environmental impact of these chemicals, ensuring they do not harm plants or animals nearby. This method should be considered as a last resort when other methods are not effective or applicable.

How to Thaw Frozen Furnace Exhaust Pipe: Thawing Techniques
Successfully thawing a frozen furnace exhaust pipe requires not only the right methods but also a cautious approach to applying these methods effectively and safely. Here are key techniques to consider:
A. Applying Heat Evenly to Frozen Section
One critical aspect of thawing is ensuring that heat is applied evenly across the frozen section of the exhaust pipe. This steady and uniform application helps melt the ice more efficiently and prevents localized overheating, which could damage the pipe. Whether using a hair dryer, heat gun, or hot towels, it is vital to move the heat source along the frozen area steadily, covering all sides if accessible. This technique allows for a uniform rise in temperature, facilitating the thawing process without causing thermal stress to the pipe.
B. Gradually Increasing Temperature to Prevent Damage
A gradual increase in temperature is imperative to avoid causing any damage to the exhaust pipe. A sudden change in temperature can lead to thermal shock, which may result in cracks or breaks in the pipe, especially if the pipe is made of materials susceptible to rapid thermal expansion. Starting with a low-heat setting and slowly moving to higher settings allows the pipe to adjust to the temperature change, minimizing the risk of damage. This approach is particularly important in severe freeze situations, where the ice’s thickness requires more prolonged exposure to heat to fully melt.
C. Using Caution to Avoid Overheating or Fire Hazards
Safety should always be a top priority when thawing a frozen exhaust pipe. Heat sources, particularly open flames, should be avoided as they pose a significant fire hazard. Even when using electric heat sources like hair dryers or heat guns, one must be cautious to prevent overheating the device or the pipe. Never leave heat sources unattended, and always monitor the pipe’s temperature to ensure it is not getting excessively hot. In addition to preventing fire hazards, this vigilance also reduces the risk of melting or deforming the pipe, which could lead to gas leaks or the need for costly repairs.
Clearing Blockages
After effectively thawing a frozen furnace exhaust pipe, it’s crucial to thoroughly clean any resultant blockages to restore proper airflow and prevent future freezing. Here’s how to address these concerns:

A. Removing Ice and Debris from Exhaust Pipe
Once the ice has melted, remnants of ice or debris may still obstruct the exhaust pipe, hindering efficient operation. To remove these, gently use a soft brush or cloth to remove any loose material. Avoid using sharp objects or metal tools that could damage the pipe’s interior. Inspect the pipe visually and, if possible, use a flashlight to check for any remaining blockages that may not be immediately visible from the pipe’s exterior.
B. Using Tools to Break Up Thick Ice Build-Up
In cases where thick ice buildup is present even after heating, it may be necessary to carefully use tools to break up the ice. Tools like plastic scrapers or a rubber mallet can be used to gently tap on the ice, facilitating its breakup without causing damage to the pipe. It’s essential to use these tools cautiously, applying minimal force to avoid denting or cracking the pipe. Always prioritize safety, wearing gloves and eye protection during this process.
C. Ensuring Unobstructed Airflow After Thawing
Finally, ensuring that airflow through the exhaust pipe is unobstructed after thawing and clearing any blockages is vital. Once you’ve removed ice and debris, conduct a flow test by turning on the furnace and feeling for air movement at the exhaust outlet. If airflow seems diminished or blocked, obstructions may still require further attention. Continuous monitoring of the exhaust pipe’s performance in the days following thawing will help identify any unresolved issues or potential for re-freezing. To minimize future freezing risks, consider installing insulation around the pipe or using heat tape with a built-in thermostat to maintain above-freezing temperatures.

Monitoring and Inspection
After taking steps to thaw a frozen furnace exhaust pipe and clearing any blockages, ongoing monitoring and inspection are crucial to ensure the problem does not recur and no secondary issues have arisen from the thawing process.
A. Checking Thawing Progress Regularly
It is important to check the progress of the thawing process regularly to ensure the ice is melting effectively and no part of the pipe is being overlooked. This involves visually inspecting the frozen section at regular intervals and feeling for cold spots that may indicate ice inside the pipe. Keeping track of how quickly the ice melts can also provide insights into the effectiveness of the chosen thawing technique and whether adjustments are needed.
B. Assessing for Any Signs of Damage or Leaks
Once the thawing process is complete, thoroughly inspecting the exhaust pipe for any signs of damage or leaks is imperative. Look for cracks, breaks, or any deformities in the pipe that may have been caused by the expansion of ice or by the heat applied during thawing. A professional should assess any damage found to determine if repairs or replacements are necessary. This step is critical to ensure the safety and proper operation of the furnace system.

C. Verifying Proper Exhaust Ventilation After Thawing
Following thawing and clearing efforts, verifying that the exhaust pipe is properly ventilating furnace gases is critical. An inadequate ventilation system can lead to a dangerous accumulation of gases such as carbon monoxide within the home. To test ventilation, turn on the furnace and check for consistent airflow from the exhaust outlet. In cases of diminished airflow, additional inspection may be needed to identify and remove any residual blockages. Continuous monitoring in the days after thawing is advised to ensure the system remains clear and functional, particularly in cold weather conditions prone to re-freezing.
Preventative Measures
Taking proactive steps to prevent the freezing of furnace exhaust pipes is essential for ensuring a smoothly operating heating system during the winter months. Here are some effective preventive measures:
A. Insulating Exhaust Pipes to Prevent Future Freezing
Insulating exhaust pipes is an effective way to reduce the risk of freezing in cold weather. Insulation materials, such as foam or fiberglass wraps, can be used to cover the pipes, helping to maintain the warmth of the exhaust gases and prevent the external cold temperatures from causing freeze-ups. When insulating, ensure that the materials are securely fastened and that there are no gaps through which cold air can enter.
B. Regularly Checking and Maintaining the Exhaust System
Regular maintenance and inspection of the furnace and exhaust system are crucial for early detection of potential issues that could lead to freezing. This involves checking for signs of wear and tear, ensuring that the exhaust pipe is free from blockages, and verifying that it is correctly installed with the proper gradient for water runoff. Scheduling an annual inspection with a heating professional can help keep the system in optimal working condition.
C. Installing Protective Devices or Heating Cables
For areas prone to extreme cold, installing protective devices such as wind guards around the exhaust outlet can help prevent freezing by reducing the impact of cold air. Additionally, heating cables can be wrapped around the exhaust pipe, providing consistent warmth to prevent ice formation. These cables are designed with built-in thermostats that activate the heat only when temperatures drop to near freezing, making them an energy-efficient preventative measure.
Professional Assistance
Professional help can be invaluable in addressing complex or persistent issues with a frozen furnace exhaust pipe and effectively implementing preventative measures.
A. Knowing When to Seek Professional Help
It’s crucial to recognize situations where professional assistance is necessary to avoid causing damage to your furnace system or endangering household safety. Professional help should be sought if the ice does not thaw after attempting DIY methods, if there is significant ice formation inside the pipe, or if any damage or leaks are detected during inspection. Additionally, if you experience recurrent freezing of the exhaust pipe despite taking preventive measures, it may indicate a more complex issue that requires expert intervention.
B. Hiring Qualified Technicians for Complex Thawing Situations
Hiring a qualified technician can ensure the job is done safely and efficiently for complex thawing situations. Professional technicians have the tools, knowledge, and experience to assess the situation accurately and apply the most effective thawing techniques. They can also identify and repair any damage that may have occurred during the freezing process. Ensure that the technician you hire is certified and has experience with furnace systems to guarantee the highest standard of service.

C. Consulting Experts for Preventative Maintenance Advice
Consulting with heating experts for preventive maintenance advice can help you understand the specific needs of your furnace system and exhaust pipe setup. Experts can offer tailored recommendations on preventing freezing in the future, assess your current preventive measures for effectiveness, and suggest improvements.
They can also guide the proper installation of insulation, heating cables, and other preventive devices to ensure they provide maximum protection against freezing. Regular consultations and maintenance checks by professionals can significantly reduce the risk of future freeze-ups, ensuring a reliable and efficient heating system throughout the winter months.

Conclusion
This guide has walked you through comprehensive steps on how to thaw frozen furnace exhaust pipe, including initial detection, safe thawing techniques using gentle heat application, and inspecting for potential damage. It emphasizes the critical nature of handling freezing issues promptly to prevent damage to your furnace system and maintain a safe home environment.
Safety and caution cannot be overstated when dealing with a frozen furnace exhaust pipe. It’s vital to approach thawing carefully, avoiding direct flames or excessive heat that can damage the pipe or create hazardous conditions. Additionally, implementing preventative measures such as insulating pipes, regular maintenance checks, and installing wind guards or heating cables drastically reduces the risk of future freeze-ups.
Understanding how to thaw a frozen furnace exhaust pipe is just one aspect of ensuring the overall functionality of your heating system. Regularly assessing the exhaust’s ventilation, adhering to safety guidelines during thawing, and engaging with professionals for advice or complex situations are key to maintaining a safe, efficient, and reliable furnace exhaust system. This approach not only prevents inconvenient and potentially dangerous freezing issues but also prolongs the lifespan of your furnace, ensuring it operates at peak efficiency throughout the colder months.

